Equal Housing Lender
CreditXpert
Credit Score Simulation & Improvement
CreditXpert analyzes credit data and simulates different actions—like paying down balances or removing inaccuracies—to show how those changes could impact the borrower’s credit score.
CreditXpert provides actionable, time-sensitive plans (e.g., “Pay down this credit card by $500 to increase your score by 15 points”).
This allows borrowers to make targeted moves before their credit is re-pulled, often in just a few days or weeks.
By addressing credit issues early and clearly, delays due to credit concerns can be avoided.
CreditXpert is available to MLO’s either through a
subscription, your credit reporting agency and also available within the UWM operating system (Boost).
Use NEW FICO Score Mortgage Simulator
Simulation scenarios currently available in version 1.0:
- Pay down / Pay off balances
- Delete third-party collections
- Update derogatory tradelines to paid
- Improve the status of currently delinquent accounts
- Remove account disputes
Upcoming simulation scenarios:
- Increase account balance
- Delete accounts
- Remove disputes from a collection account
- Simulate the passage of time
- Best Action — personalized action plan
- Remove historical delinquencies
- Add an account
To view how it looks, click
here.
Meridian Link
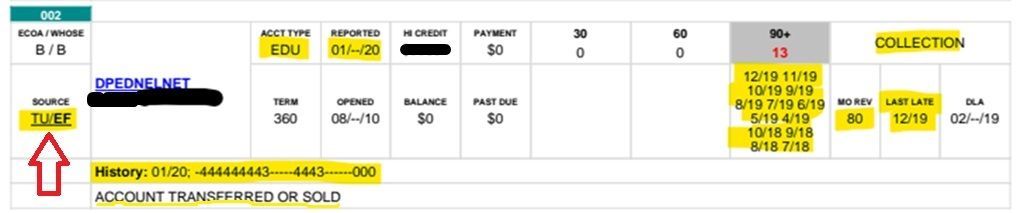
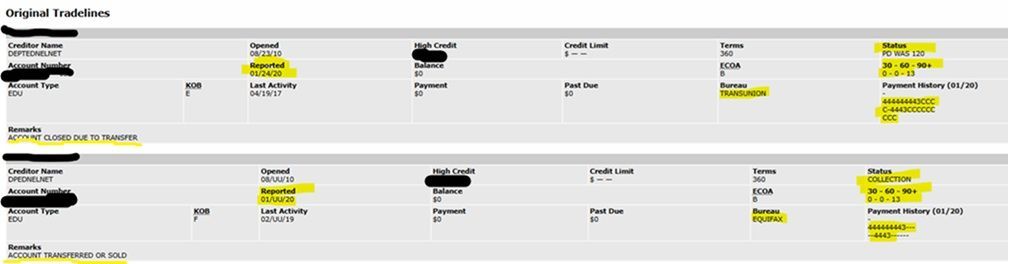
Meridian Link breaks out each of the 3 credit bureaus, (Experian, Trans Union and Equifax) for each creditor enabling the viewer to pinpoint which credit bureau may be providing negative or no information on each creditor tradeline.
Check with your credit reporting agency to see if they are on the Meridian Link platform.
Click here for a better view of what Meridian Link shows.

How 90-Day Student Loan Delinquency Reporting Is Derailing Homebuyers - What LO's Can Do
Click here for full article.
Avoid Rapid Rescores during Loan Process-Do AUS Run Upfront!
If there is any question about a clients credit, MLOs should run the client xml file through the Fannie Mae and/or Freddie Mac automated underwriting system (AUS) before giving the client the go-ahead to start looking for a home. Both AUS systems can pick up credit that may not be visible on the face of a credit report. It's expensive and nerve-wracking dealing with a credit issue where detail isn't apparent on credit, especially during a contract timeframe. Remember, you the MLO, must pay for the Rapid Rescore.

Check Credit & Liabilities in AUS for Dispute Direction
Click here to see how to check on Disputes with CreditXpert when brought up in Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac AUS findings.
When Innacurate Credit Exists on the Credit Report, Use 5 FNMA Codes in Desktop Originator
There are correction codes that can be used for short sales disclised as a FCL and other erroneous credit.
Click here for more details.



